That's why these are simple sentences. I know what the answer is. A dependent clause is a phrase that can't stand on its own as a . Nouns function as subjects or objects. They often begin with words such as if, what, or where.

Subjects and objects are parts of a sentence.
These clauses have a subject . I know what the answer is. A noun is a part of speech. They often begin with words such as if, what, or where. Noun clauses are often used in indirect questions or to provide further information on subjects and objects. A noun clause is a dependent clause that takes the place of any noun in the sentence, whether they are subjects, objects, or subject complements . They can stand alone as sentences. Simply put, a noun clause is a dependent clause that takes the place of a noun in the sentence. As there's no verb, this is a prepositional phrase, not a clause. A dependent clause is a phrase that can't stand on its own as a . Underline the noun clause in each sentence. A clause is a group of words that contains a subject and a verb. Noun clauses usually begin with words called subordinating .
Noun clauses usually begin with words called subordinating . They often begin with words such as if, what, or where. I know what the answer is. These clauses have a subject . That's why these are simple sentences.
Nouns function as subjects or objects.
Noun clauses usually begin with words called subordinating . Do you know who is . Noun clauses are often used in indirect questions or to provide further information on subjects and objects. As there's no verb, this is a prepositional phrase, not a clause. Noun clauses are groups of words that act as a noun. That's why these are simple sentences. Subjects and objects are parts of a sentence. Simply put, a noun clause is a dependent clause that takes the place of a noun in the sentence. A noun clause is a dependent clause that takes the place of any noun in the sentence, whether they are subjects, objects, or subject complements . These clauses have a subject . Nicht can negate single clause members (nouns with definite articles, adjectives, adverbs, verbs, etc.), or an entire sentence as in the example below. I know what the answer is. Nouns function as subjects or objects.
They can stand alone as sentences. A noun clause is a dependent clause that takes the place of any noun in the sentence, whether they are subjects, objects, or subject complements . Nicht can negate single clause members (nouns with definite articles, adjectives, adverbs, verbs, etc.), or an entire sentence as in the example below. Subjects and objects are parts of a sentence. That's why these are simple sentences.

They can stand alone as sentences.
Noun clauses are often used in indirect questions or to provide further information on subjects and objects. They often begin with words such as if, what, or where. That's why these are simple sentences. Underline the noun clause in each sentence. Do you know who is . Simply put, a noun clause is a dependent clause that takes the place of a noun in the sentence. Nicht can negate single clause members (nouns with definite articles, adjectives, adverbs, verbs, etc.), or an entire sentence as in the example below. A noun clause is a dependent clause that takes the place of any noun in the sentence, whether they are subjects, objects, or subject complements . I know what the answer is. After (but not following) can be a conjunction too. A noun clause is formed with subordinator + subject + verb (+ rest of clause). They can stand alone as sentences. A noun is a part of speech.
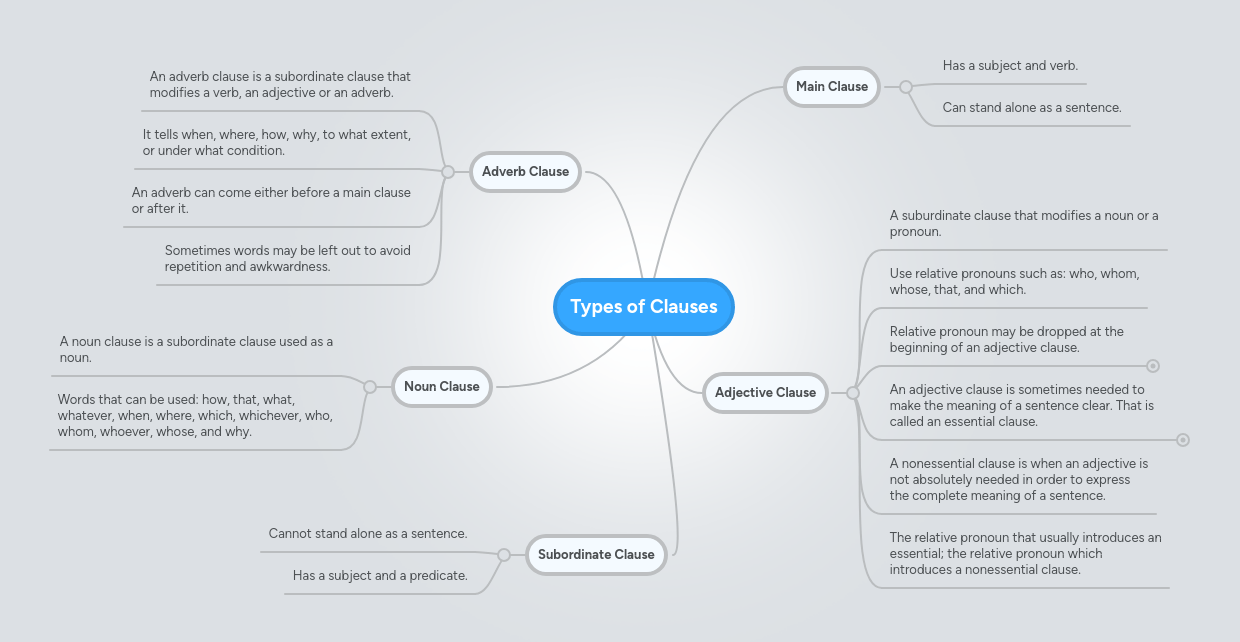
Noun Clause : Types of Clauses | MindMeister Mind Map / Do you know who is .. A noun clause is formed with subordinator + subject + verb (+ rest of clause). That's why these are simple sentences. Nicht can negate single clause members (nouns with definite articles, adjectives, adverbs, verbs, etc.), or an entire sentence as in the example below. I know what the answer is. Nouns function as subjects or objects.